Immune system (part 1)
Immune system
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
• Molecules, cells, tissues and organs which provide non-specific and specific protection against
• Microorganisms
• Microbial toxins
• Tumor cells
– Crucial to human survival
ORIGIN OF CELLS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
• Derived from common progenitor cell in bone marrow
– Pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell
• Progenitor Stem Cells
– Myeloid lineage
• Monocyte/macrophage, dendritic cells, PMN’s, mast cells
• Erythroid : Erythrocytes and Megakaryocytes
– Lymphoid lineage
• Small and large lymphocytes
Hematopoietic stem cell
GATA transcription factors are a family of transcription factors characterized by their ability to bind to the DNA sequence "GATA“
Oct-2 is a octamer transcription factor which is part of the POU family.
POU (pronounced 'pow') is a family of proteins that have well-conserved homeodomains. The acronym POU
is derived from the names of three transcription factors:
the Pituitary-specific Pit-1
the Octamer transcription factor proteins Oct-1 and Oct-2 (octamer sequence is ATGCAAAT)
the neural Unc-86 transcription factor from Caenorhabditis elegans
CELLS OF INNATE AND ADAPTIVE
IMMUNITY
– Myeloid Lineage
– Referred to as
• Polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN’s)
– Nuclei are multilobed (2 to 5)
• Granulocytes
– Cytoplasmic granules
– Neutrophil: Principal phagocytic cell of innate immunity
– Eosinophil: Principal defender against parasites
– Basophil: Functions similar to eosinophils and mast cells
Neutrophils and macrophages
• Phagocytes - travel throughout body in pursuit of invading
pathogens
• Neutrophils are found in bloodstream ; most abundant
phagocyte, normally representing 50% to 60% of circulating
leukocytes
• During acute phase of inflammation, particularly as a result of
bacterial infection, neutrophils migrate toward site of
inflammation in a process called chemotaxis, and are usually
first cells to arrive at scene of infection
• Macrophages are versatile cells that reside within tissues and
produce a wide array of chemicals including enzymes,
complement proteins, and regulatory factors such as
interleukin 1
• Macrophages also act as scavengers, ridding body of worn-out cells and other debris, and as antigen-presenting cells that
activate adaptive immune system
Eosinophils
• Kills Ab-coated parasites through
degranulation
• Involved in allergic inflammation
• A granulocyte
• Double Lobed nucleus
• Orange granules contain toxic
compounds
Basophils
• Might be “blood Mast cells’
• A cell-killing cells
– Blue granules contain toxic and
inflammatory compounds
• Important in allergic reactions
CELLS OF INNATE AND ADAPTIVE
IMMUNITY
• Myeloid lineage
– Monocytes
• Leukocytes with bean shaped or brain-like
convoluted nuclei
• Circulate in blood with half life of 8 hours
• Precursors of tissue macrophages
– Macrophages
• Mononuclear phagocytic cells in tissue
• Derive from blood monocytes
• Participate in innate and adaptive immunity
CELLS OF INNATE AND ADAPTIVE
IMMUNITY
• Myeloid lineage
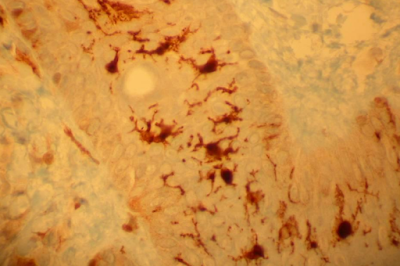
– Dendritic cells
• Cells with dendriform (star shaped) morphology
• Interdigitating reticular cells (synonym)
• Capture and present antigens to T lymphocytes
– Mast cells
• Located in mucous membrane and connective tissue
throughout body
• Major effectors cell in allergy
• Modulation of initial immune response
to be continue
Disclaimer:
The content provided in this article is based on personal knowledge and educational background in the fields of health and nutrition. It is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. For any health concerns, please consult a qualified healthcare provider .
The content provided in this article is based on personal knowledge and educational background in the fields of health and nutrition. It is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered a substitute for professional medical advice. For any health concerns, please consult a qualified healthcare provider .
































Comments
Post a Comment